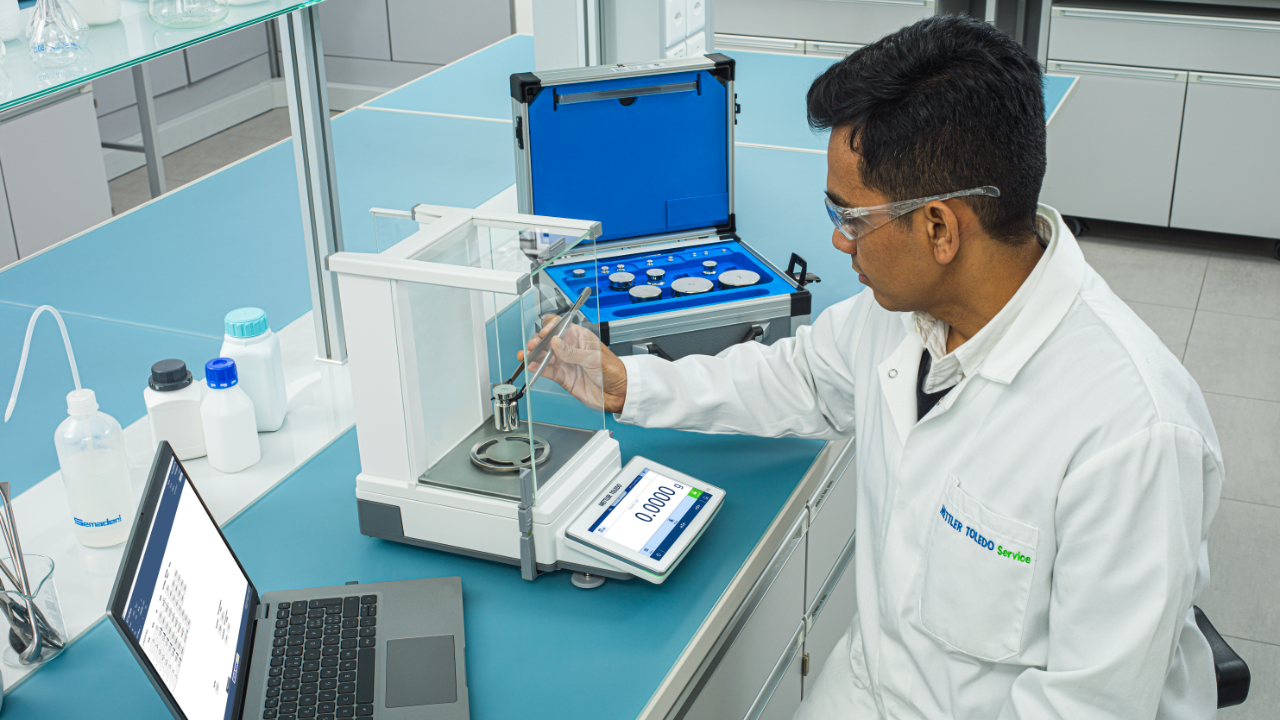
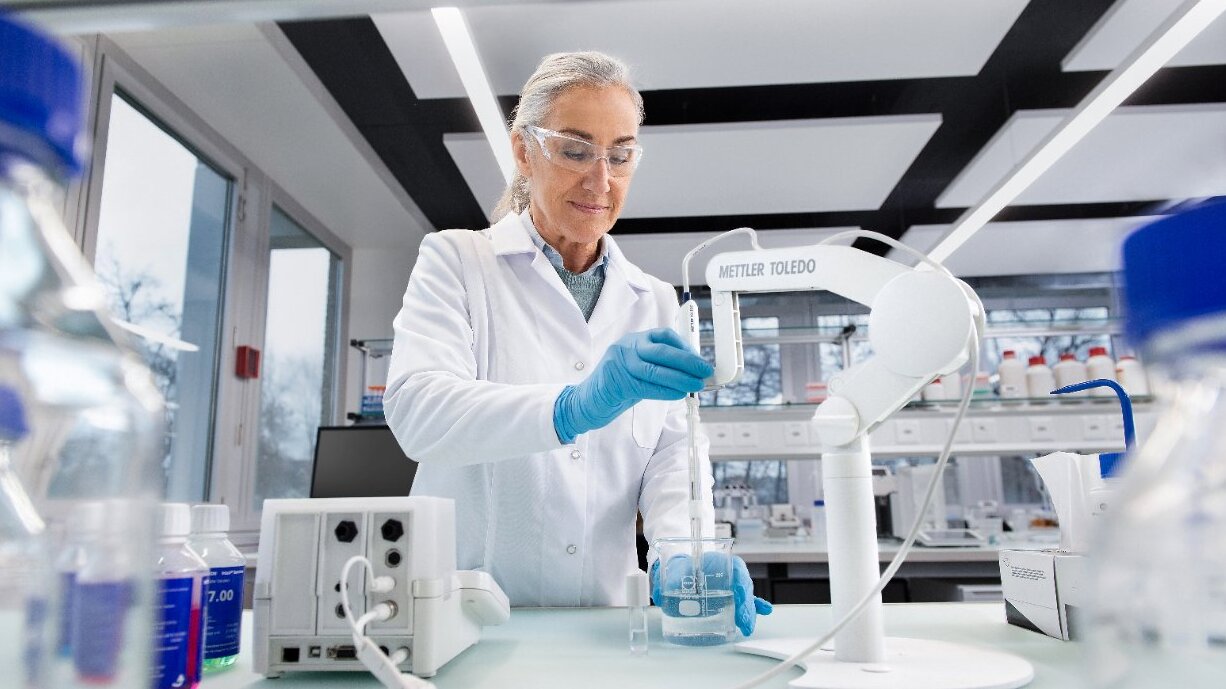
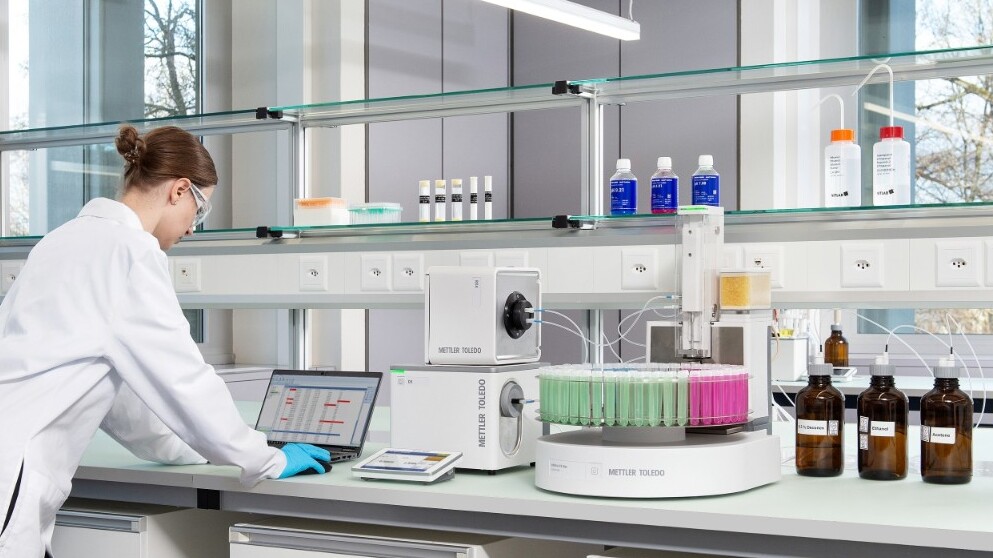
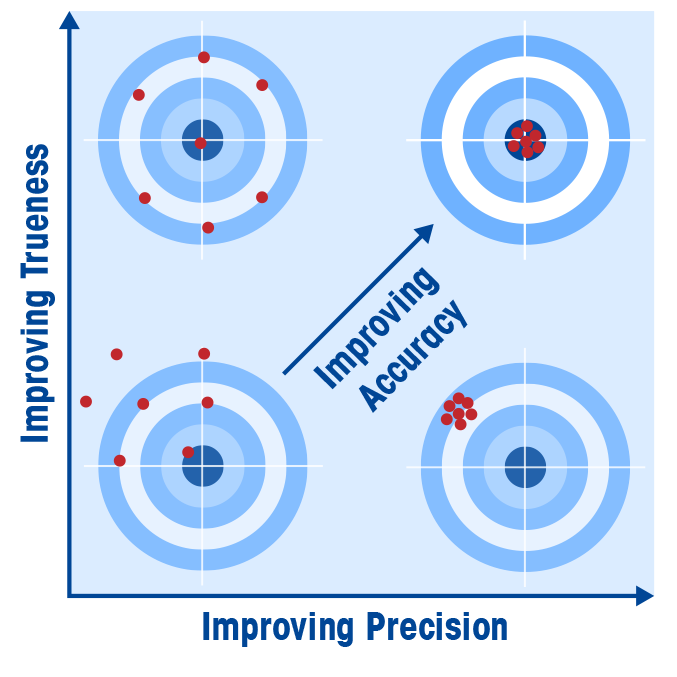
Calibration involves testing an instrument at multiple measurement points across its operational range. A METTLER TOLEDO Service Technician carefully evaluates deviations to ensure the instrument operates within acceptable tolerances. These deviations can result from:
- Normal wear and tear
- Misuse or mishandling
- Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity
- Electrical interference
Calibration schedules are determined through risk assessment, considering factors like instrument criticality, usage frequency, and regulatory requirements. High-risk instruments or instruments used in critical processes often require more frequent calibration to maintain measurement integrity.
Calibration steps include:
- As-Found calibration: Performed before maintenance to document initial accuracy
- Adjustment (if needed): Corrections are made if the instrument is out of tolerance
- As-Left calibration: Conducted after maintenance and potential adjustments to verify that the instrument meets specifications
Regular calibration is vital for quality control. It ensures ongoing measurement accuracy and compliance with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and various Pharmacopoeia standards. By proactively calibrating instruments, labs avoid costly errors, regulatory violations, and unreliable data.
If deviations exceed acceptable tolerances, adjustments may be necessary to bring the instrument back into compliance.