 |
In today's fast-paced world, ensuring the integrity and quality of your laboratory data is paramount.
Fortunately, there are existing standards that describe useful processes.
Our comprehensive guide offers essential insights and tips for maintaining data accuracy, security, and compliance in your thermal analysis workflow based on proven principles.
These tips can be applied in any industry where result quality matters.
Why Data Integrity Matters
Data integrity is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s a fundamental aspect of scientific reliability. Inaccurate or mishandled data can lead to erroneous conclusions, wasted resources, and potential legal challenges. By adhering to established guidelines, you can safeguard your data and reinforce the credibility of your results.
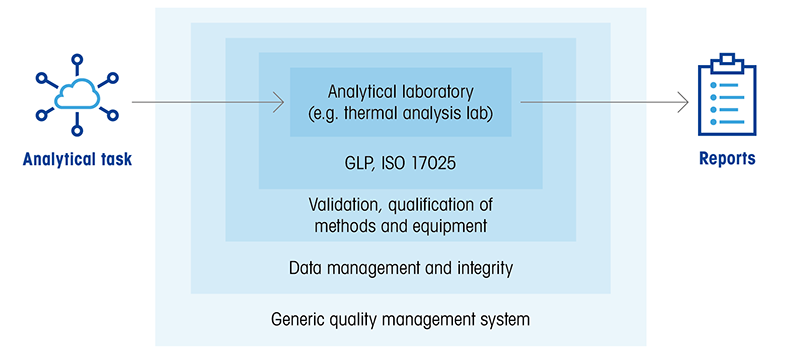 |
Figure: Layers of compliance for any analytical laboratory |
The Impact of Data Integrity on Business
ALCOA+ Principles
Understanding the key principles of data integrity is essential:
Attributable | When creating a record, the identity of the person or computer system that collected or generated the data has also to be recorded together with the date and time of the recording. |
Legible | Data must be readable and understandable during the retention time of the record. |
Contemporaneous | Records of an activity have to be made at the time it takes place. This is relevant for handwritten records. |
Original | Records should be original rather than copies or transcriptions. This affects mostly written records. |
Accurate | Records should reflect the reality of what happened and should be error free. Original information should be unedited. Data are correct, truthful, complete, valid, and reliable. |
Complete | All recorded data requires an audit trail to show nothing has been deleted or lost. |
Consistent | Data should be recorded chronologically, e.g. each record is date and time stamped in the expected order. |
Enduring | Data must be stored in a safe way. |
Available | All records are accessible or retrievable for review, audit, or inspection over the lifetime of the record. |
Data Management Best Practices
Effective data management is crucial for maintaining data integrity throughout its lifecycle:
- Data Entry Protocols: Establish standard operating procedures (SOPs) for data entry to minimize human error.
- Automated Systems: Utilize electronic data capture (EDC) systems that have built-in checks and balances to enhance data accuracy and reduce manual entry errors.
- Version Control: Implement a version control system for data to track changes and ensure that the most current information is always accessible.
- Data Backup: Regularly back up data to prevent loss due to hardware failure or cyberattacks. Consider using cloud storage solutions for enhanced security.
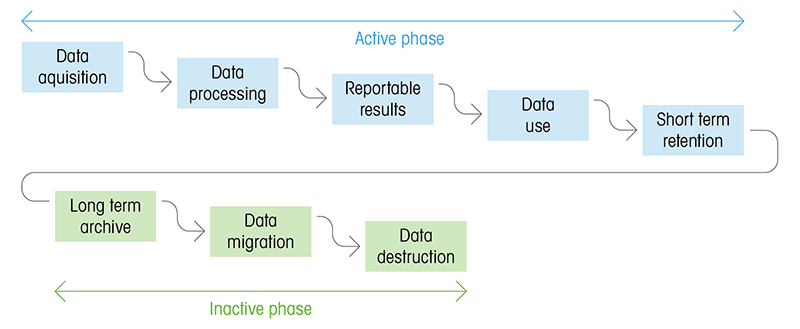 |
Figure: Active and inactive phases of data. Time wise the inactive phase is far longer than the active phase. Data migration is therefore an important and crucial aspect for the long-term accessibility of data during the inactive phase. |
Compliance Guidelines
Understanding the regulatory framework is essential:
- 21 CFR Part 11: This regulation by the FDA addresses the use of electronic records and electronic signatures in a manner equivalent to paper records. Familiarize yourself with the requirements to ensure compliance.
- Data Audit Trails: Implement systems that automatically generate audit trails. These logs should capture all actions related to data, including who accessed it, what changes were made, and when they occurred.
- Training and Education: Regularly train staff on data integrity principles and compliance requirements. Knowledgeable employees are your first line of defense against data integrity breaches.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance plays a pivotal role in maintaining compliance and preventing data mishandling:
- Regular Audits: Schedule regular audits of data management processes to identify weaknesses and areas for improvement. Audits can help ensure compliance and foster a culture of accountability.
- Corrective and Preventative Actions (CAPA): Establish a CAPA process to address data integrity issues promptly. This system should document the issue, root cause analysis, and steps taken to prevent recurrence.
- Quality Control Checks: Implement routine quality control checks to ensure that data integrity is upheld in every stage of data management.

