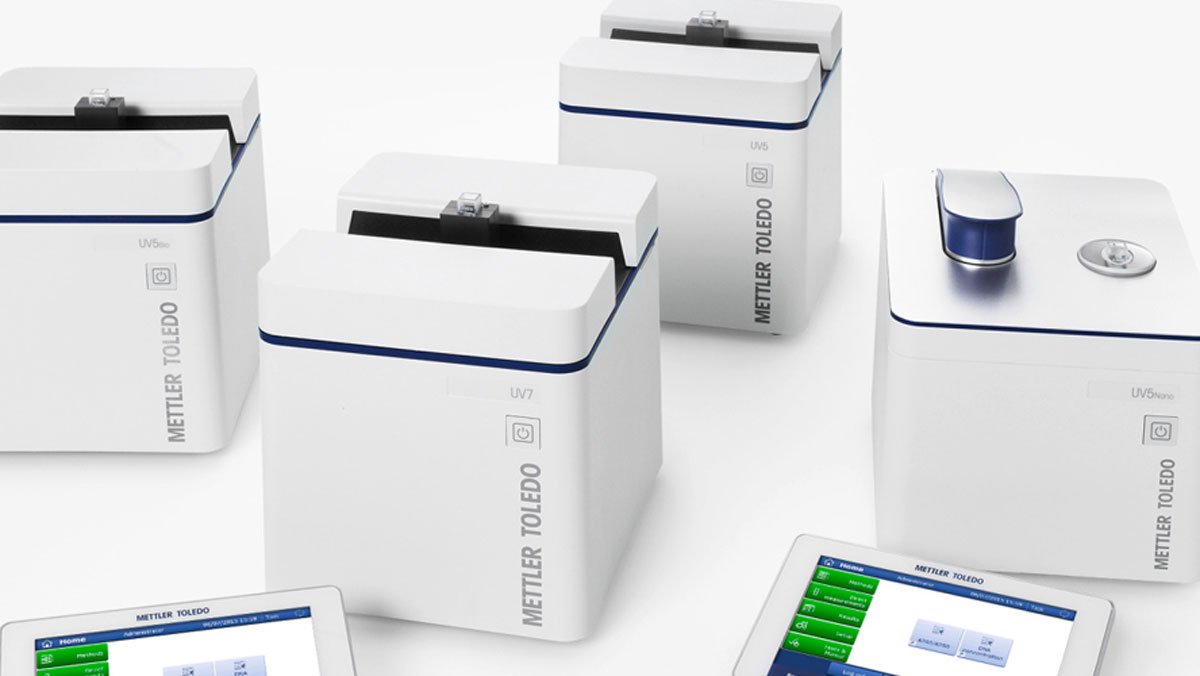
Spectrometers for Chemical Analysis
Chemical Analysis Made Easy with Our Intuitively Designed UV Vis Spectrophotometers
Advantages for Chemical Applications
Small, Fast, Simple and Reliable
METTLER TOLEDO'S UV/VIS Excellence Spectrophotometers offer a range of benefits to optimize and simplify your spectrophotometric analysis workflow. Watch the video and learn more about our UV Vis instruments.
30 Most Common Color Numbers
For similar samples, one number can be sufficient to express the color. Depending on the industry, different color numbers are established. METTLER TOLEDO spectrophotometers provide 30 built-in different color scales.

Simple One Click Operation
An easy and intuitive way to run tasks right from the terminal. Get secure guidance with step-by-step instructions. Customizable shortcuts are easily linked directly on the home screen.
Find out More About Our UV/Vis Spectrophotometer Lines
Useful Related Links
UV Vis Accessories
Optimize your spectroscopic workflow using our smart accessories, such as a cuvette changer, autosampler, thermostat, etc.
Color Measurement
Understand the science behind color and its critical role in various applications. Discover how our spectrophotometers ensure consistent color quality and find the right instrument for your needs!
UV Vis Software
Data acquisition, storage, and display are efficiently supported by UV Vis PC software. Result data can also be automatically exported or seamlessly integrated into a centralized data management system (e.g. LIMS).
UV Vis Autosampler
Choose between the Flex, Pro, and Max UV Vis InMotion™ autosampler base, and combine it with a sample rack. Finish your system with a UV Vis sample kit to make it the perfect fit for your laboratory.
UV Vis Cuvettes
The METTLER TOLEDO cuvette portfolio offers reliable and economic macro glass cuvettes in 10 and 50 mm optical path length (OPL), Micro Cuvettes and Flow Cells.
UV Vis Publications
Find our publications in the topics of UV Vis spectrophotometric fundamental, applications, instrumentation, pharmacopeia compliance, etc.
Unlock Service Excellence - Maximize Your Efficiency

Unlock Service Excellence - Maximize Your Efficiency
FAQ
What is spectrometry in chemical analysis?
Spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique used to identify and quantify the components of a sample based on their interaction with light. In chemical analysis, spectrometry involves measuring the intensity of light absorbed or emitted by a sample at specific wavelengths.
Spectrometry has a wide range of applications in chemical analysis. It is used to quantify components in substances, ensuring the purity and consistency of products, monitoring pollutants in the environment, and more.
What is a spectrometer used for in chemistry?
A spectrometer is a crucial instrument in the chemical industry, used to measure the intensity of light as a function of wavelength. It's a versatile tool with applications across various fields, including:
- Quantitative Analysis: Determining the concentration of a specific substance in a solution by measuring the amount of light it absorbs or transmits.
- Qualitative Analysis: Identifying the presence of specific compounds based on their unique absorption or emission spectra.
- Kinetic Studies: Monitoring the rate of chemical reactions by measuring the change in absorbance over time.
- Environmental Monitoring: Analyzing pollutants in water and soil by measuring their absorbance spectra.
What does a spectrophotometer do in chemistry?
A spectrophotometer is an essential analytical instrument in chemistry that measures the intensity of light absorbed or transmitted by a sample at specific wavelengths.
Spectrophotometers have a wide range of applications across various fields, including pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and biochemistry. They are commonly used for quantitative analysis, such as measuring glucose levels in blood samples, monitoring reaction rates in kinetics studies, and assessing the purity of chemical compounds without destroying the sample.
Their ability to provide fast and accurate results makes them invaluable in laboratories, helping scientists and researchers make informed decisions based on precise data.
How does a chemical spectrometer identify different compounds?
A chemical spectrometer identifies different compounds by analyzing their unique absorbance spectrum of light. When a sample is illuminated, specific wavelengths of light are absorbed or emitted by the molecules within the compound. The intensity of this absorption or emission is directly related to the compound's molecular structure.
The spectrophotometer separates the light into its individual wavelengths and measures their intensity. This data is then plotted to create a spectrum, which shows the intensity of light absorbed or emitted at different wavelengths.
By comparing the obtained spectrum to known reference spectra, analysts can identify the compounds present in the sample. Each compound has a distinct spectral fingerprint, characterized by unique peaks at specific wavelengths. This allows for both qualitative (identifying the presence of specific compounds) and quantitative (determining the concentration of compounds) analysis.
What is the range of wavelengths used in chemical spectrometry?
In chemical spectrometry, the range of wavelengths typically spans several electromagnetic spectrum regions, depending on the specific technique. Here are the main ranges:
- Ultraviolet (UV) Spectrometry
Wavelengths: Approximately 200 to 400 nm.
Used for analyzing electronic transitions in molecules, particularly for compounds with conjugated systems. Visible (Vis) Spectrometry
Wavelengths: Approximately 400 to 700 nm.
Focuses on color and is commonly used in colorimetry for identifying and quantifying colored compounds.
- Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectrometry
Wavelengths: Approximately 700 to 2500 nm.
Useful for analyzing molecular vibrations and is often applied in food and agricultural chemistry. - Mid-Infrared (MIR) Spectrometry
Wavelengths: Approximately 2500 to 25,000 nm (or 4000 to 400 cm⁻¹).
Widely used in infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) for identifying functional groups in organic compounds. - Raman Spectrometry
Wavelengths: Typically uses lasers in the visible to near-infrared range (400 to 800 nm) for analyzing molecular vibrations. - Mass Spectrometry
While not based on light absorption, it can analyze ions generated from samples, which often correspond to specific wavelengths in other spectroscopic methods.
Each of these ranges is tailored to different types of molecular interactions, making them suitable for specific analytical applications in chemistry.
METTLER TOLEDO’s spectrophotometers support ultraviolet (UV) and visible (Vis) spectrometry
What safety precautions should be taken when using a chemical spectrometer?
Chemical spectrometers, while powerful tools for analysis, can pose potential hazards if not used correctly.
Here are some essential safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Wear Appropriate PPE: This includes lab coats, safety glasses, gloves, and potentially respiratory protection, depending on the chemicals being analyzed and solvents being used.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Ensure that your workspace is adequately ventilated to reduce exposure to potentially harmful fumes, especially when using volatile solvents.
- Familiarize Yourself with Chemicals: Before starting your work, read the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all chemicals involved in your analysis to understand their hazards and proper handling procedures.
- Use a Fume Hood: When handling volatile solvents or hazardous reagents, perform all sample preparations and dilutions inside a fume hood to minimize inhalation risks.
- Sample Preparation: Use mechanical or electronical pipettes to avoid mouth pipetting. Ensure that all pipettes and sample holders are clean and free from residual contaminants.
- Utilize Automated Features: To minimize human exposure to chemicals you can equip your spectrophotometer with automation accessories, e.g. sipper pumps or autosampler.
- Proper Storage: Store all chemicals used with the spectrometer in designated, labeled cabinets. Ensure incompatible substances are stored separately to prevent reactions.
- Labeling: Clearly label all sample vials and reagent containers with relevant hazard information and the date of preparation.
- Waste Disposal: Follow laboratory procedures for disposing of chemical waste. Ensure that waste containers are clearly labeled and that hazardous waste is collected for proper disposal.
- Maintain Equipment Regularly:
- Regularly check the spectrometer for signs of wear, leaks, or malfunctions. Report any issues to the laboratory supervisor immediately.
- Clean the exterior of the instrument and sample compartments according to manufacturer instructions to prevent contamination and damage.
- Ensure that all electrical connections are secure and that the instrument is grounded to prevent electrical hazards.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of accidents and ensure a safe working environment when using a chemical spectrometer.
- Automated UV/Vis Spectrophotometer Calibration
- Color Spectrophotometers
- Microvolume Spectrophotometer
- Single-Beam Spectrophotometers
- Spectrophotometer for Pharma
- Spectrophotometers for DNA Analysis
- Spectrophotometers for Water Analysis
- UV Spectrometers
- UV/VIS Autosampler
- UV/Vis Cuvettes for Spectrophotometers
- UV/Vis Spectrophotometer
- UV/Vis Spectrophotometer Accessories